A Clean Water Pump Must Be a Sustainable Pump. It Must Be Readily Available and Easily Maintained With Parts That Are Locally Accessible
A clean water pump must be a sustainable pump. Maintenance should be easily accomplished with a little training, and parts for the pump must be readily available at a local level.
Hand-powered pumps are used worldwide to deliver water from borehole wells. Drilling borehole wells and installing hand pumps has long been a low cost and reliable strategy for meeting the clean water needs of rural communities in developing countries.
Borehole wells have been shown to provide the safest source of water for a community.
This is partly due to the filtering capacity of the gound through which water passes as it percolates into the aquifer. It is also due to the well driller's ability to sanitize the wells and to seal off the water source from surface contamination. See Groundwater and associated pages.

Relief and development organizations have installed thousands of hand pumps all over the world in the last twenty to thirty years.
Unfortunately, the lack of a sufficient program providing for clean water pump sustainability and upkeep has left many (if not most) of these hand pumps in a state of neglect and disrepair.
It is estimated that 30-45% of all hand pumps installed break within ten years. Many of these remain broken due to a lack of skills, tools, and parts to repair them.
Wells are of no use without a functioning clean water pump, so many communities lose their water supplies when the pumps break or quit working due to neglect or a lack of parts.
Sometimes all that is needed to restore a water supply is some fairly simple training in hand pump operation and hand pump repair and a responsible party to undertake pump maintenance and repair.
A local pump repair program can improve access to clean water by simply repairing and maintaining pumps that are already installed, but are not working.
Water for People has launched the FLOW app. for Android which people in the developing world can use to instantly broadcast reports about whether their water and sanitation projects are working or failing. This simple phone app introduces a new level of transparency, efficiency, and accountability to their work.
The World of the Clean Water Pump Can Be Divided Into Two Categories:
Proprietary Pumps
and
Public Domain Pumps
Proprietary pumps can only be manufactured by licensed manufacturers.
These pumps are patented and the rights to manufacture and sales are protected. Parts for these pumps must be purchased from the manufacturer or a licensed distributor.

Public domain pumps, on the other hand, can be manufactured by anyone, and anyone can sell parts for public domain pumps.
The manufacture and distribution of public domain pumps is not protected by patents or intellectual property rights.
The open licensing of public domain pumps makes them generally more available and cheaper than proprietary pumps. Hand pump components are more widely available and more than one company manufactures them.
In this clean water pump repair section we will focus on public domain pumps.
There are a myriad of proprietary pumps in use around the world. The general pump repair procedures discussed in this section will apply to any kind of clean water pump, public domain or proprietary.
However, procedures and practices that may be specific for a particular proprietary pump will not be discussed.
In practice, when you come across a proprietary pump, if you do not know how to repair it, or if you do not have a repair manual for the specific pump, or if you are not able to get parts for that pump; it is best not to attempt a repair. Doing so may create more problems than it solves.
For instance, you may be able to pull the pump out of the well, but not be able to repair it. You might be left with the pump in pieces, unable to assemble it for lack of parts.
You would then have to make a decision about whether to put the pump back in the well or replace it with another pump.
Trying to fix any pump without the knowledge, expertise, and parts to do so may only make a bad situation worse.
In this section we will be focus on the following public domain pumps:
Afridev Hand Pump
India Mark II and India Mark III Hand Pumps
Bush Pump
Tara Direct Action Hand Pump
"SlapShot" Hand Pump
Treadle Pump

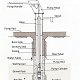
All of the above listed pumps are considered “lift” pumps in that the pump cylinder containing the pump piston is located below the water table and water is lifted up the riser main with the action of the piston.
This is different than a “suction” pump that has the pump cylinder above ground and draws water from the well through suction rather than through lift.
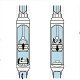
The Afridev hand pump , India Mark II pumps ,and India Mark III pumpsare considered "lift" pumps and also "piston" pumps.
The indirect action of the pump lever acting on the pump rod and the piston assembly provides adequate force to lift a heavy column of water (plus the weight of the pump rod) from a deep well.
These hand pumps are also available in Deep Well configurations for applications greater than 15 meters (50 feet).
The parts of deep well hand pumps are either cast or machined steel. This heavy duty construction is required to accommodate the greater forces involved in lifting the heavier water column and pump rod from a deep well.
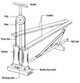
Bush Pumps are made from readily available and common hardware and plumbing parts and the name “Bush Pump” actually describes the above-ground parts of the pump.
Below ground, these pumps may utilize an Afridev or India Mark II or Mark III riser and pump cylinder or some kind of proprietary pump.
Above ground, the pump is designed to be easy to fabricate and easy to maintain.

Tara Pumps are public domain pumps that are limited to more shallow wells.
They are considered “direct action” pumps. There is no pump lever and the weight of the column of water must be directly lifted by the human operator.
The advantage of Tara pumps is that, unlike the other pumps listed above, water is brought to the surface during both the upstroke and the downstroke of the pump handle.
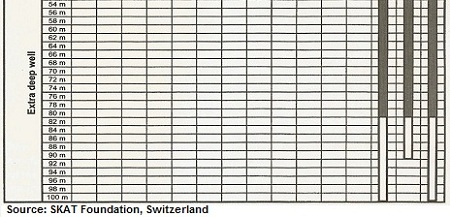
The factor that limits the maximum depth of any clean water pump is the pump’s ability to support the weight of the column of water and the pump rod.
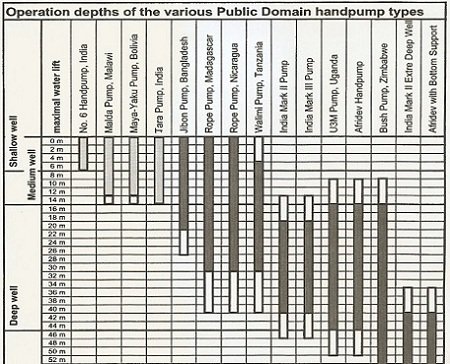
The chart below indicates the recommended operation depths of the pumps listed above, as well as other public domain hand pumps.
One other clean water pump that is very easy to build and maintain, is the"SlapShot" Hand Pump designed by Hydromissions. This pump is built of common plumbing parts and can be made very cheaply.
Treadle pumps are more often used for agricultural purposes than for supplying drinking water, but they are included here because they are so prevalent in India and Southeast Asia. They can be used like any other suction pump and have the same limitations as those types of pumps have.
Swiss Centre for Development Cooperation in Technology and Management (SKAT) publishes a water pumping manual entitled "Water Lifting".
The PDF file is available here and includes information on a wide range of water pump topics.
RSWN publishes a Hand Pump Technical Guide as well:
The PDF file is available here and also includes information on a wide range of water pump types.
Return "Home" from "Clean Water Pump"